- March 6, 2024
- Comment: 0
- Blog
What are the best treatments for gum disease?
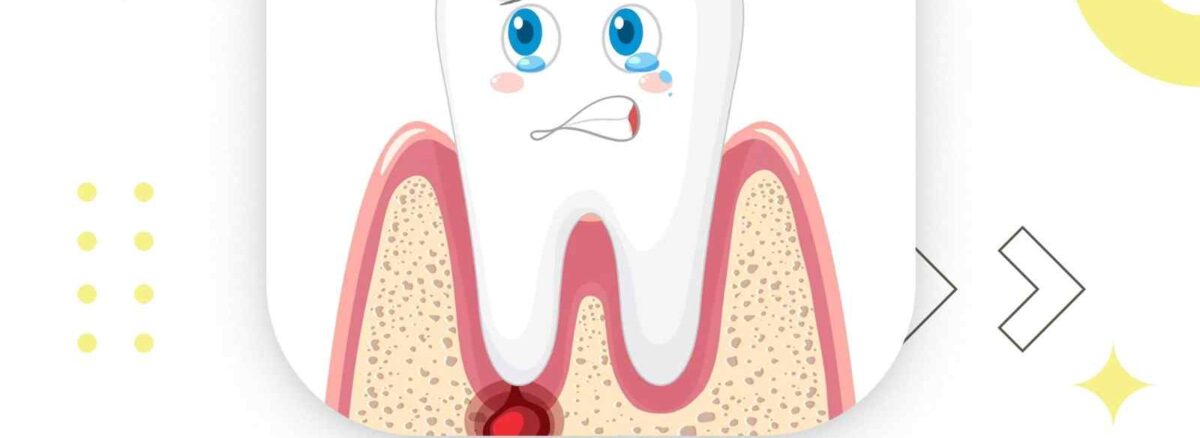
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. From mild gingivitis to severe periodontitis, gum disease can have serious consequences if left untreated. In this article, we’ll explore the best treatments for gum disease, ranging from non-surgical interventions to advanced surgical procedures.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It typically starts as gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. Without proper treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, where the infection spreads deeper into the gums and bone, leading to tooth loss. Symptoms of gum disease include gum recession, persistent bad breath, loose teeth, and gum abscesses.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Gum Disease
- Professional Dental Cleaning:
The first line of defense against gum disease is professional dental cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing. During this procedure, the dentist removes plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and roots, smoothing the tooth surfaces to prevent bacteria from reattaching.
- Antibiotic Therapy:
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate bacterial infections and reduce inflammation in the gums. Antibiotics can be administered orally or applied directly to the affected area.
- Dental Procedures:
For more severe cases of gum disease, dental procedures such as gingival flap surgery and laser therapy may be recommended. These treatments aim to reduce pocket depths, remove diseased tissue, and promote gum tissue regeneration.
Surgical Treatments for Advanced Gum Disease
- Dental Implant:
In cases where tooth loss has occurred due to advanced gum disease, dental implants may be recommended as a long-term solution for replacing missing teeth. Dental implants are titanium posts that are surgically inserted into the jawbone and topped with artificial teeth, providing a stable and natural-looking restoration.
- Gum Graft Surgery:
Gum graft surgery involves taking tissue from elsewhere in the mouth or using donor tissue to cover exposed tooth roots and restore gum tissue lost to recession.
- Bone Grafts and Guided Tissue Regeneration:
In cases where gum disease has caused bone loss around the teeth, bone grafts and guided tissue regeneration techniques may be used to regenerate bone and promote tissue regrowth.
- Pocket Reduction Surgery:
Also known as flap surgery, pocket reduction surgery involves lifting the gums to access and clean the roots of the teeth. The gums are then repositioned to reduce pocket depths and facilitate healing.
Maintenance and Aftercare
After undergoing gum disease treatment, it’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent recurrence. This includes brushing and flossing daily, using antimicrobial mouthwashes, and attending regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and adopting a healthy diet can also support gum health.
Alternative and Adjunctive Treatments
While conventional treatments are the mainstay of gum disease management, some individuals may explore alternative or adjunctive therapies. Herbal remedies, natural supplements, and specific mouthwashes containing antimicrobial ingredients may offer additional benefits in conjunction with standard treatments.
Future Trends and Research
Researchers are continually investigating new treatments and technologies to improve gum disease management. From probiotics and stem cell therapy to advanced imaging techniques and targeted drug delivery systems, the future holds promise for more effective and personalized approaches to treating gum disease.
Gum disease is a serious oral health condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to prevent complications such as tooth loss and systemic health problems. By understanding the best treatments available, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their gums and preserve their overall oral health.
By implementing a combination of non-surgical interventions, surgical procedures, and comprehensive aftercare, individuals can effectively manage gum disease and enjoy a healthy smile for years to come. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to successful gum disease management, so don’t hesitate to seek professional dental care if you notice any signs or symptoms of gum disease.